National Hydrogen Mission: A Step-by-Step Guide to India’s Green Energy Revolution
 |
| National Hydrogen Mission, green hydrogen, hydrogen energy in India, renewable energy, green energy transition, hydrogen economy, India’s energy goals |
.............Introduction..............
The National Hydrogen Mission (NHM), launched on 15th August 2021 by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, represents India's ambitious effort to transition towards a sustainable and clean energy future. As global concerns about climate change escalate, India has committed to achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2070. The hydrogen mission is central to this goal, promoting the production and usage of green hydrogen to decarbonize various sectors like industry, transport, and power.
This article provides a step-by-step breakdown of the National Hydrogen Mission, its goals, implementation strategy, and impact. Let's dive deep into India’s green hydrogen roadmap.
Watch itStep 1: Understanding What Green Hydrogen Is
Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe. However, producing pure hydrogen requires separating it from other elements, often through chemical or electrochemical processes.
Types of Hydrogen Based on Production Method:
Grey Hydrogen: Produced from natural gas or coal, emits CO₂.
Blue Hydrogen: Grey hydrogen + carbon capture and storage.
Green Hydrogen: Produced through electrolysis using renewable energy (like solar or wind), zero carbon emissions.
The National Hydrogen Mission focuses exclusively on green hydrogen due to its eco-friendly nature and potential to cut down fossil fuel dependence.
Step 2: Setting the Vision and Goals
The National Hydrogen Mission’s primary objectives are:
1. Become a global hub for green hydrogen production and export.
2. Reduce dependency on imported fossil fuels.
3. Decarbonize heavy industries and transportation.
4. Boost job creation in the green energy sector.
5. Enhance energy security through indigenous production.
Targets under the Mission
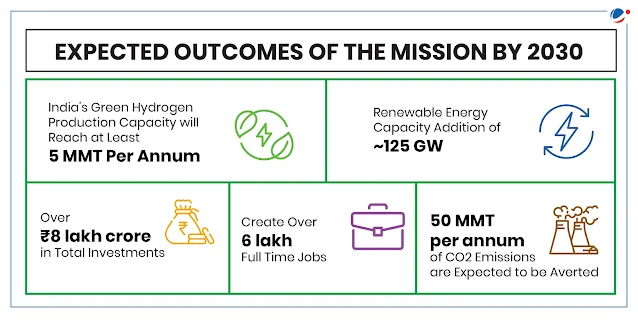
5 Million Metric Tonnes (MMT) of green hydrogen production annually by 2030.
125 GW of renewable energy capacity addition for hydrogen production.
Promote green hydrogen across sectors: fertilizers, refineries, steel, and transport.
Step 3: Policy Framework and Phased Implementation
The National Hydrogen Mission is being implemented in phases, focusing on creating demand, building supply, and supporting infrastructure development.
Phase-I (2022–2026): Laying the Foundation
Demand creation in government-run industries (like fertilizer and petroleum).
Initial production capacity targets.
Development of pilot projects in various sectors.
Launch of Green Hydrogen Policy (2022) to facilitate open access to renewable power.
Phase-II (2026–2030): Scaling Up
Expand green hydrogen use in private industries and public transportation.
Encourage exports to energy-deficit countries.
Strengthen research & innovation.
Develop an ecosystem of electrolyzers, storage systems, and hydrogen fueling stations.
Step 4: Key Components of the National Hydrogen Mission
1. Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT)
Financial incentives for green hydrogen and electrolyzer manufacturing.
Budget allocation of ₹19,744 crores under this initiative.
..... ...Split into two parts:
SIGHT-I: Incentives for green hydrogen production.
SIGHT-II: Support for domestic electrolyzer manufacturing.
2. Public-Private Partnerships (PPP)
Collaborations with private players to build hydrogen infrastructure.
Encouraging Indian and foreign investments in the hydrogen sector.
3. Pilot Projects
Trials in long-haul trucking, railways, shipping, and steel production.
Testing of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) in real-time scenarios.
.................4. Hydrogen Hubs
Designating specific regions as Hydrogen Hubs where production, storage, and distribution infrastructure is concentrated.
States like Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, and Rajasthan leading the way.
Step 5: Green Hydrogen Policy 2022 – Key Provisions
The government announced the Green Hydrogen Policy in February 2022 to provide regulatory clarity and support.
Major Provisions:
Open access for renewable energy for green hydrogen production within 15 days.
Banking of renewable energy for 30 days.
Waiver of inter-state transmission charges for 25 years.
Land allotment in renewable parks to set up hydrogen plants.
Priority grid connectivity to green hydrogen projects.
This policy plays a critical role in attracting investments and expediting project implementation.
Step 6: Industrial and Transport Sector Integration
1. Industrial Sector
Steel: Hydrogen-based direct reduced iron (DRI) methods to replace coal.
Fertilizer: Green ammonia from green hydrogen as an alternative to natural gas.
Refineries: Use hydrogen for desulfurization, replacing grey hydrogen.
...................2. Transport Sector
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs): Offer long-range, fast refueling, ideal for commercial use.
Indian Oil, NTPC, and Ashok Leyland are testing hydrogen buses and trucks.
Development of hydrogen refueling stations across key highways.
Step 7: Global Collaborations and Export Potential
India’s green hydrogen has the potential to emerge as a major export commodity. With its vast renewable energy capacity and cost competitiveness, India can serve countries like Japan, Germany, and South Korea.
Collaborations:
India-EU Hydrogen Partnership.
Bilateral ties with countries like Australia, UAE, and Norway.
Participation in International Hydrogen Trade Forums.
Step 8: Technological Innovation and R&D
Establishment of Hydrogen Innovation Centers.
Support for startups and research institutions working on:
Efficient electrolysis methods.
Hydrogen storage and safety.
Fuel cell technologies.
The government encourages R&D through grants, tax benefits, and academic partnerships.
Step 9: Challenges in Implementation
Despite the promising vision, several challenges remain:
1. High cost of electrolyzers and green hydrogen production.
2. Lack of storage and transportation infrastructure.
3. Limited technical expertise and skilled manpower.
4. Safety concerns related to hydrogen handling.
5. Need for long-term policy stability.
However, with robust planning and global support, these barriers can be overcome.
Step 10: The Road Ahead – Future Prospects
With the National Hydrogen Mission in full swing, India is poised to:
Reduce 3.6 gigatonnes of CO₂ emissions by 2050.
Save ₹1 lakh crore annually in fossil fuel imports.
Generate 6 lakh+ new jobs in the green hydrogen ecosystem.
Become a global hydrogen export hub by the 2030s.
........Conclusion
The National Hydrogen Mission marks a bold and strategic shift in India's energy policy. It leverages renewable resources, promotes economic growth, and addresses the climate crisis head-on. With a structured and phased roadmap, India aims to lead the global green hydrogen economy, setting an example for sustainable development.
Whether you're a policymaker, investor, or curious citizen, now is the time to engage with India’s hydrogen revolution.
More details reading and Watching
1. PIB
2. https://mnre.gov.in/en/national-green-hydrogen-mission/
4.
........................FAQs...................
Q1. What is the National Hydrogen Mission?
It is a government initiative launched in 2021 to promote the production and use of green hydrogen in India.
Q2. Why is green hydrogen important?
Because it produces zero carbon emissions and can decarbonize hard-to-abate sectors.
Q3. What are the targets of the mission?
Produce 5 MMT of green hydrogen annually and add 125 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030.
Q4. Who are the major players involved?
Public and private sectors including NTPC, IOCL, Reliance, Adani, and global partners.
Q5. What are the benefits of green hydrogen?
Clean energy, reduced emissions, job creation, and energy independence.
Here are some trivia and interesting facts about hydrogen, the lightest and most abundant element in the universe:
Basic Trivia
1. Symbol & Atomic Number: Hydrogen’s symbol is H and its atomic number is 1 .it’s the first element on the periodic table.
2. Lightest Element: It is the lightest and simplest element, consisting of just one proton and one electron.
3. Abundance: About 75% of the universe’s elemental mass is hydrogen. It powers the stars, including our Sun, through nuclear fusion.
Scientific Facts
4. Forms of Hydrogen:
Protium (¹H): The most common isotope (1 proton, 0 neutrons).
Deuterium (²H): Used in nuclear reactors and scientific research.
Tritium (³H): Radioactive and used in nuclear fusion and glow-in-the-dark products.
5. Highly Flammable: Hydrogen gas is extremely flammable and was infamously involved in the Hindenburg disaster (1937).
6. No Color or Smell: Pure hydrogen is colorless, odorless, and tasteless.
Industrial & Practical Uses
7. Rocket Fuel: Hydrogen is used in rocket propulsion—liquid hydrogen combined with liquid oxygen produces immense thrust.
8. Green Energy: Hydrogen is being explored as a clean fuel alternative for vehicles and power plants.
9. Ammonia Production: It’s a key ingredient in making ammonia (NH₃) via the Haber-Bosch process, essential for fertilizers.
Cultural & Historical Facts
10. Discovery: English scientist Henry Cavendish discovered hydrogen in 1766 and called it “inflammable air.”
11. Name Origin: The name hydrogen comes from Greek hydro (water) and genes (creator)—“water-former”—because it forms water when burned.
12. First Element in the Big Bang: Hydrogen was the first element formed after the Big Bang, making it nearly 13.8 billion years old.






No comments:
Post a Comment